Predicting the Future with AI-powered Predictive Maintenance
- Home
- Case Study
- Predicting the Future with AI-powered Predictive Maintenance
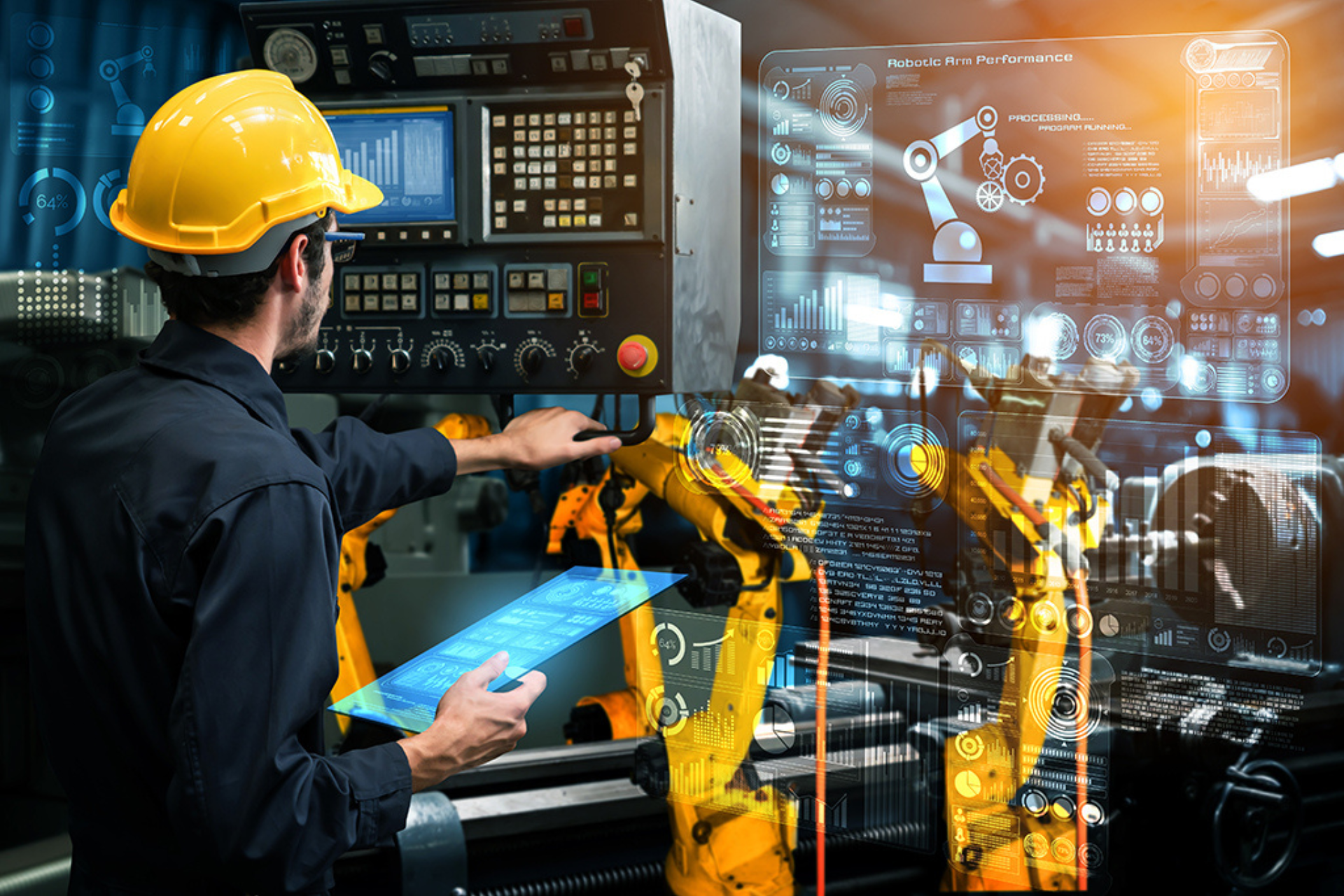

Imagine a world where factories hum with uninterrupted productivity, where machines whisper warnings of potential issues before they escalate into costly breakdowns. This is the reality promised by Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the form of Predictive Maintenance (PdM).
Traditional maintenance relies on reactive repairs, fixing problems only after they occur. This leads to production downtime, lost revenue, and potential safety hazards. Predictive Maintenance, however, takes a proactive approach, utilizing AI to monitor equipment health and predict failures before they happen.
How AI Makes Predictive Maintenance Possible
AI, specifically machine learning, thrives on data. In PdM, this data comes from a network of sensors embedded in machinery. These sensors collect real-time information on various parameters like vibration, temperature, and energy consumption.
The AI model then analyzes this data, recognizing patterns and anomalies that might signal impending equipment failure. Here's a breakdown of the process:
Data Acquisition: Sensors continuously collect data from equipment, feeding it into the AI system.
Machine Learning Algorithms: The AI model is trained on historical data of equipment performance and known failure scenarios.
Anomaly Detection: The model identifies deviations from normal operating parameters, suggesting potential problems.
Predictive Analysis: Based on the identified anomalies and historical data, the model predicts when a failure is likely to occur.
Benefits of AI-powered Predictive Maintenance
Reduced Downtime: By proactively addressing potential issues, AI-powered PdM minimizes unplanned equipment failures and production disruptions.
Lower Maintenance Costs: Focusing resources on targeted maintenance based on AI predictions reduces unnecessary repairs and maintenance overhauls.
Improved Safety: Early detection of equipment problems prevents catastrophic failures, minimizing safety hazards for workers.
Optimized Production Planning: Predictive maintenance allows for proactive scheduling of maintenance activities, ensuring smooth production flow and increased overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Real-world Applications of AI in PdM
AI-powered PdM is making waves across various industries:
Manufacturing: AI monitors factory machinery, predicting issues in assembly lines, robots, and critical production equipment.
Energy Sector: AI can predict potential failures in power plants, wind turbines, and electrical grids, preventing blackouts and ensuring reliable energy production.
Transportation: AI helps monitor the health of airplanes, trains, and ships, enabling proactive maintenance and ensuring safe transportation.
Challenges and Considerations
Data Quality and Integration: Reliable and high-quality data from sensors is crucial for accurate AI predictions. Integrating data from various sources can be complex.
Implementation Costs: Setting up an AI-powered PdM system requires investment in sensors, data infrastructure, and AI expertise.
Change Management: Integrating AI into existing maintenance workflows requires buy-in from personnel and addressing potential concerns about job displacement.
The Future of AI in Predictive Maintenance
The future of AI in PdM is bright. We can expect advancements in:
Edge Computing: Processing sensor data closer to the source (on the equipment itself) will enable faster response times and real-time decision making.
Advanced Analytics: Emerging AI techniques like deep learning will lead to even more accurate predictions and earlier detection of potential issues.
Integration with IoT (Internet of Things): AI-powered PdM will seamlessly integrate with the broader IoT ecosystem, allowing for real-time monitoring and remote maintenance capabilities.
Conclusion
AI-powered Predictive Maintenance is transforming the industrial landscape. By embracing this technology, companies can optimize production processes, minimize downtime, and ensure long-term equipment health. As AI continues to evolve, the future of maintenance is not about fixing problems, but about predicting and preventing them altogether.